How to Change Text Color in CSS
Code Playground is only enabled on larger screen sizes.
We discussed CSS selectors and how they allow us to target specific HTML elements in the previous lesson. Now, let’s explore what we can do with those selected elements.
A great starting point is changing the color.
In this lesson, we’ll delve into different ways to modify colors in CSS. You’ll learn how to use color names, HEX codes, RGB values, and HSL formats to style text effectively.
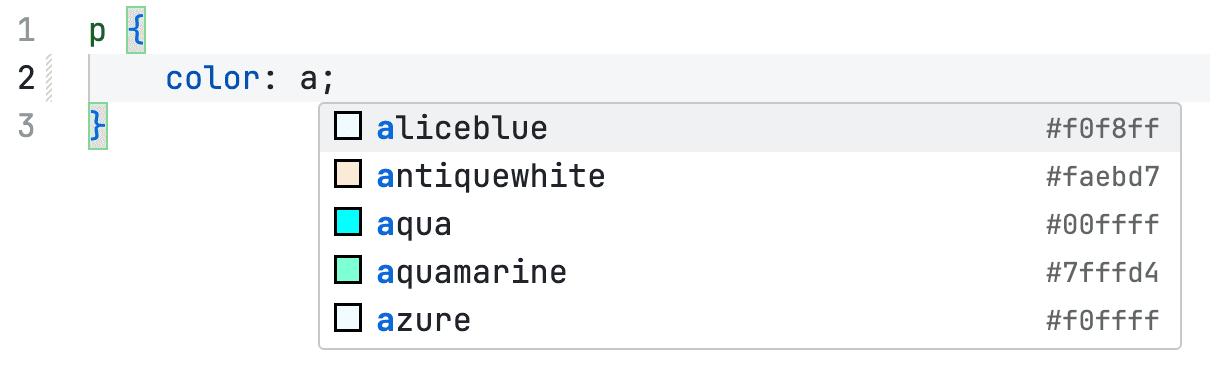
As demonstrated before, after selecting a <p> element, you can change the text color by specifying a color property.
p {
color: red;
}Or change the element's background color using the background-color property:
p {
background-color: darkorange;
}The color property accepts descriptive color names such as red, darkorange, and so on.
However, there are so many different colors in the world, and not all of them has a name. That is why CSS offers more accurate ways of specifying colors, including RGB, HEX, and HSL.
RGB color
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue. They are the fundamental colors in computer science, and when mixed together, they can create every color in the world.
The RGB color is defined with the function rgb():
rgb(<red>, <green>, <blue>)The parameters red, green, and blue define the intensity of each color, using integer values between 0 and 255. 0 is the weakest, and 255 is the strongest.
For example, the following example is the same as color: red;.
p {
color: rgb(255, 0, 0);
}If you mix the colors together, you will be able to create all kinds of different colors.
p {
color: rgb(168, 189, 45);
}It is recommended that you use a color picker to help you find the desired color. It is difficult to visualize the mixed color just from the numbers.
There is also a sibling function called rgba(), which takes an extra parameter.
p {
color: rgba(<red>, <green>, <blue>, <alpha>);
}The last parameter, alpha, defines the transparency of the element. It accepts values from 0 to 1. 0 being completely transparent, and 1 being completely solid.
p {
color: rgba(167, 189, 45, 0.408);
}HEX color
HEX colors are specified with a hexadecimal number like this:
#rrggbbThe hex color code always starts with a #, and it is essentially a shorthand for the rgb() formula.
Each variable, rr, gg, and bb, accepts a hex value from 00 to ff, which corresponds to decimal numbers from 0 to 255.
For example:
p {
color: #ff0000;
}This is the same as color: rgb(255, 0, 0); and color: red;.
Similarly, you can specify an alpha value to control the transparency of the element.
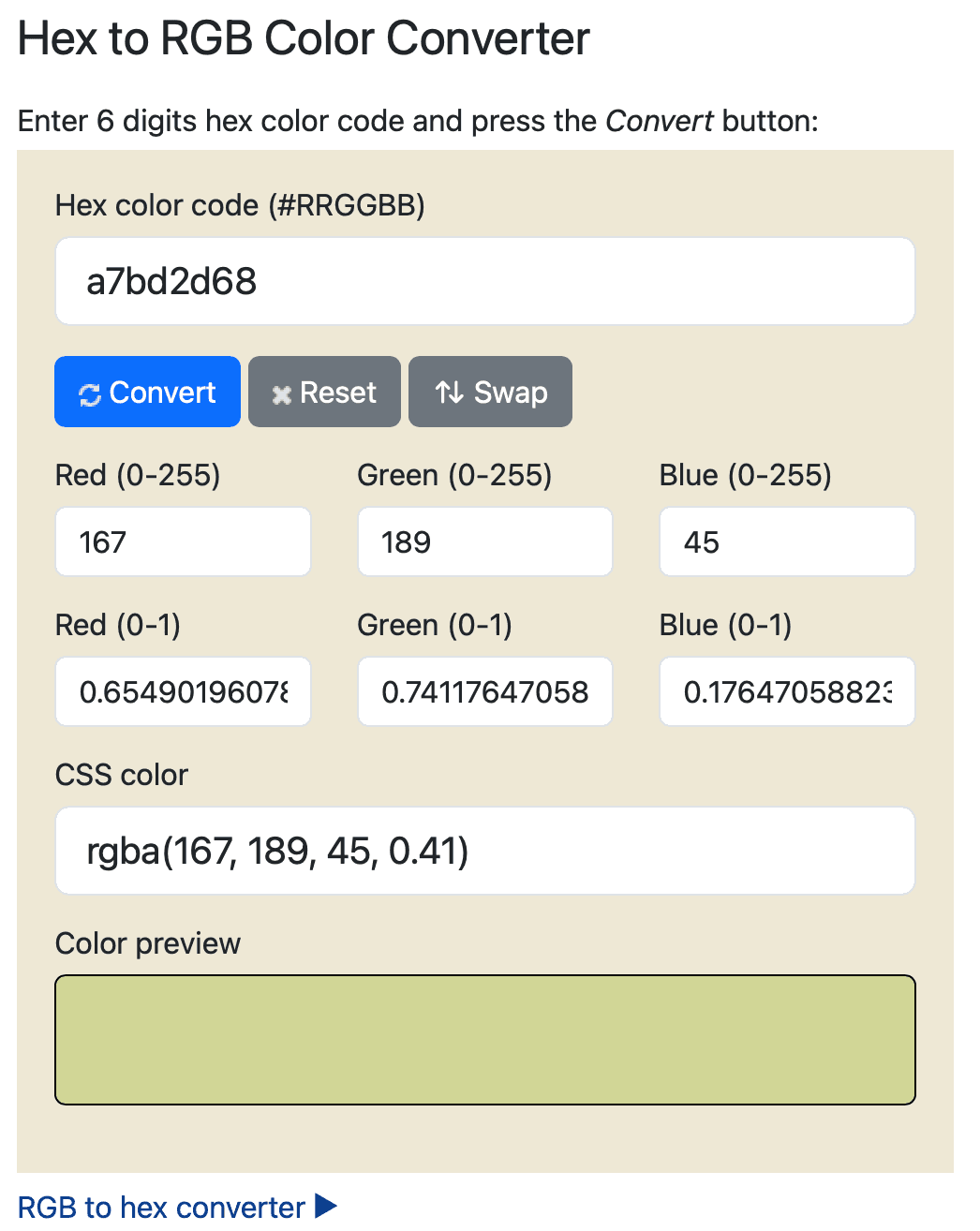
#rrggbbaaaa also takes values from 00 to ff, which are remapped to decimal values between 0 and 1.
p {
color: #a7bd2d68;
}This is the same as rgba(167, 189, 45, 0.408). You can verify that with this tool.
HSL color
If you are familiar with graphic design, you probably already know this color model. HSL takes three variables:
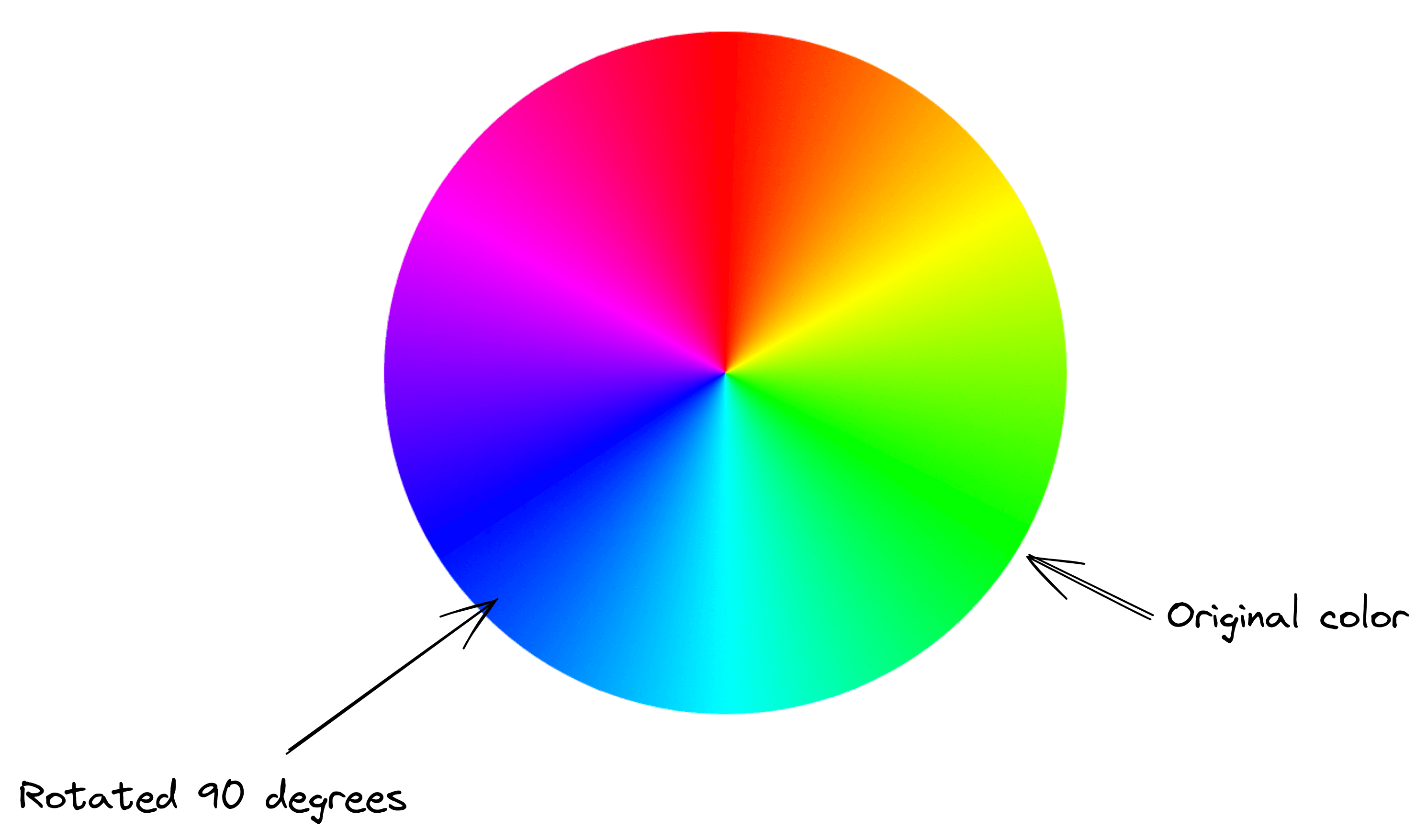
hsl(<hue>, <saturation>, <lightness>)hue is the degree on a color wheel, from 0 to 360. A color wheel looks like this:
Notice that this wheel has no black, white, or gray. That is the job for the parameters saturation and lightness.
saturation takes a percentage value, from 0 to 100, which determines how much gray should be added to the original color. 0 means the color is completely gray, and 100 means no gray is added.
lightness is also a percentage value, which determines how much black or white is added to the original color.
Lastly, hsla() is a similar formula that allows you to define an alpha value, which controls the transparency of the element.
hsla(hue, saturation, lightness, alpha)p {
color: hsla(69, 62%, 46%, 0.408);
}This example is the same as #a7bd2d68 and rgba(167, 189, 45, 0.408).
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/styles.css"> </head> <body> <p>Hello, World!</p> </body> </html>