Fundamentals of Full-Stack Development: A Beginner’s Guide
Code Playground is only enabled on larger screen sizes.
Full-stack development is the process of creating both the frontend and the backend part of an application.
It involves designing the web app's appearance, implementing the functionalities, deploying to the server, and optimizing and scaling the app to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
This roadmap walks you through the fundamentals of building web applications.
Together, we are going to cover everything you need to know to become a full-stack developer, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, as well as frameworks such as Express.js, React.js, and Next.js.
What is a web application
A web application is an interactive software program that runs in a web browser, allowing users to perform tasks and interact with dynamic content over the internet.
Unlike traditional desktop or mobile applications, web apps do not need to be installed on a user's device and can be used across various platforms and devices.
What is the frontend
A web application can be split into two parts: the frontend and the backend.
The frontend is the part of a website that users can see and interact within their browser.
When you enter a URL and press Enter, the interface that you see is the frontend. It is usually built using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
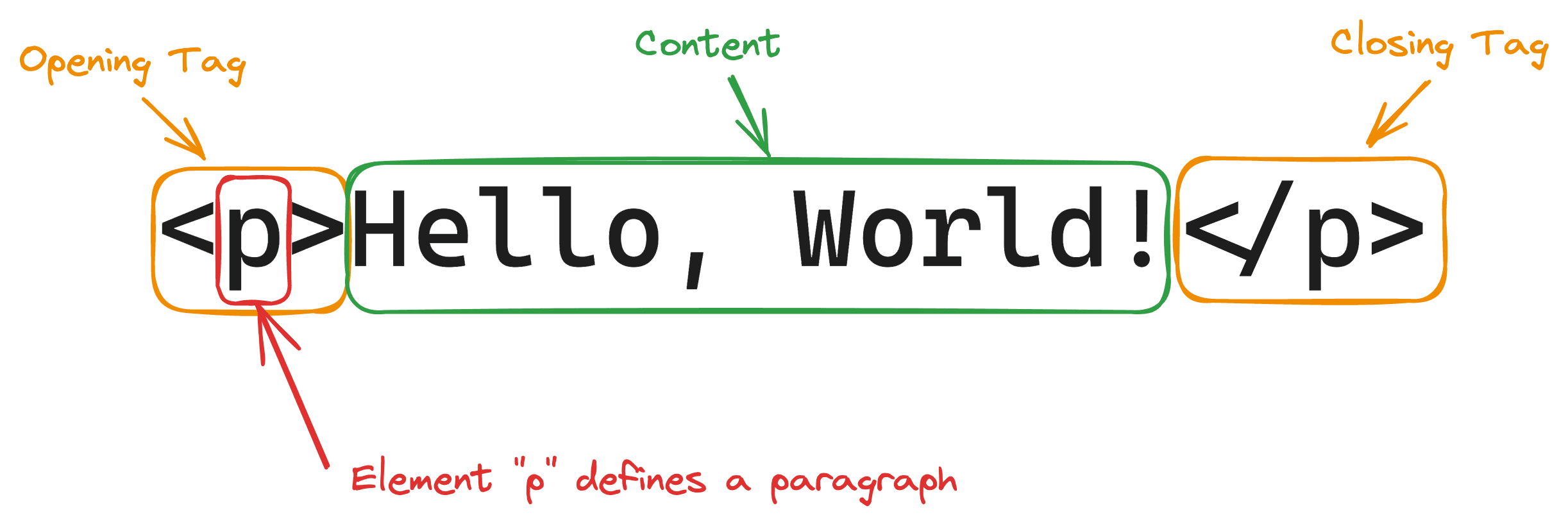
HTML defines the structure and content of a webpage using HTML elements, which are usually made of an opening tag, content, and a closing tag.
The name of the tag specifies the element type, and you can add additional information by assigning extra attributes.
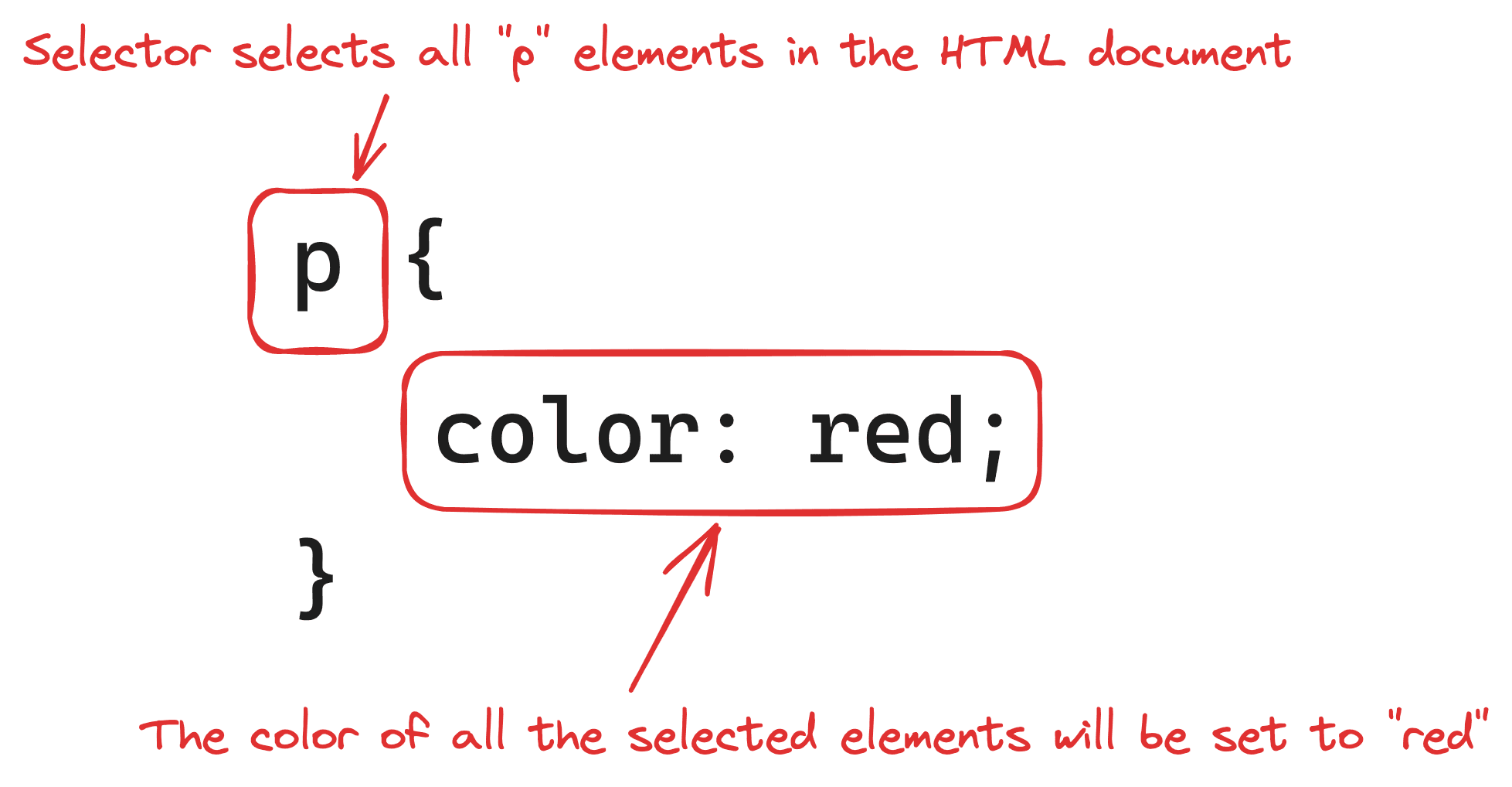
CSS defines the appearance of the HTML elements. It is made of a selector and a set of style rules in key/value pairs.
The example above selects all <p> elements, and apply the style rule color: red;.
Sometimes, you might need more interactivity for your webpage, such as a pop-up menu or an image that zooms in when clicked. That's where JavaScript shines.
As a demonstration, the example in the Code Playground creates a square that moves back and forth when the corresponding button is clicked.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#demo {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
position: absolute;
left: 5px;
top: 40px;
transition: all 0.5s linear;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="moveDiv()">Move</button>
<button onclick="returnDiv()">Return</button>
<div id="demo">
<div>
<script>
function moveDiv() {
document.getElementById("demo").style.left = "400px";
}
function returnDiv() {
document.getElementById("demo").style.left = "5px";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Implementing something like this does require decent programming skills, we are going to come back to this topic after covering JavaScript first.
What is the backend
If a web application only delivers fixed webpages defined by HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, it is called a static web application.
However, imagine you are building a blog app with hundreds of articles. Making so many static pages would be a tedious task.
When you need to make a design change on the website, you'll have to apply the same changes to hundreds of document, making your app impossible to maintain in the future.
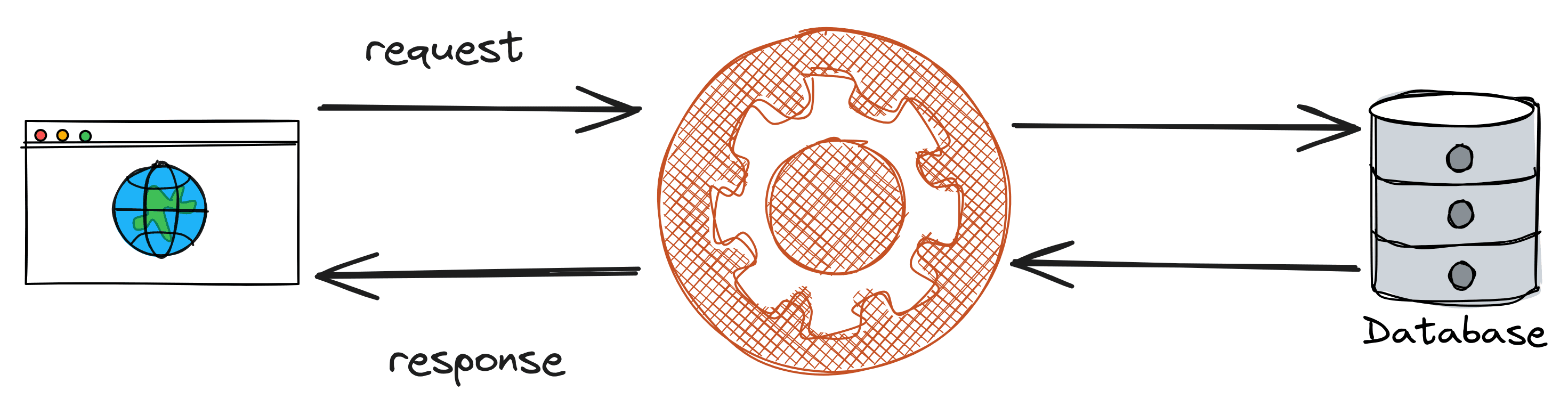
A better way to do this is to store the articles inside a database, which can easily and safely store millions of records, and then create a backend application in charge of retrieving information from that database.
The backend app then uses the retrieved data to generate static pages and serve to the user.
Such applications are referred to as dynamic web applications.
The backend program can be written in many different languages, such as JavaScript, Python, PHP, Java, and more. For this course, we are going to use JavaScript, as it is the only one that works in both the frontend and the backend.
In this roadmap, we are going to cover:
- The fundamentals of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
- Backend development with JavaScript
- Frontend development with React.js
- Full-stack development with Next.js
- Creating AI apps powered by OpenAI, or any other ML model providers
Practicing is always the best way of learning.
So, along the way, we are going to create real app, from calculators and todo lists, to SaaS platforms and AI chatbots.
Without further ado, let's get started!
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Document</title> <style> #demo { width: 100px; height: 100px; background: red; position: absolute; left: 5px; top: 40px; transition: all 0.5s linear; } </style> </head> <body> <button onclick="moveDiv()">Move</button> <button onclick="returnDiv()">Return</button> <div id="demo"> <div> <script> function moveDiv() { document.getElementById("demo").style.left = "400px"; } function returnDiv() { document.getElementById("demo").style.left = "5px"; } </script>